Gun carrying over the life course:
Onset, continuity, and exposure to gun violence from adolescence to early adulthood
| Charles C. Lanfear | University of Cambridge |
| Rebecca Bucci | Harvard University |
| David S. Kirk | University of Oxford |
| Robert J. Sampson | Harvard University |
Gun homicide is mostly handgun homicide
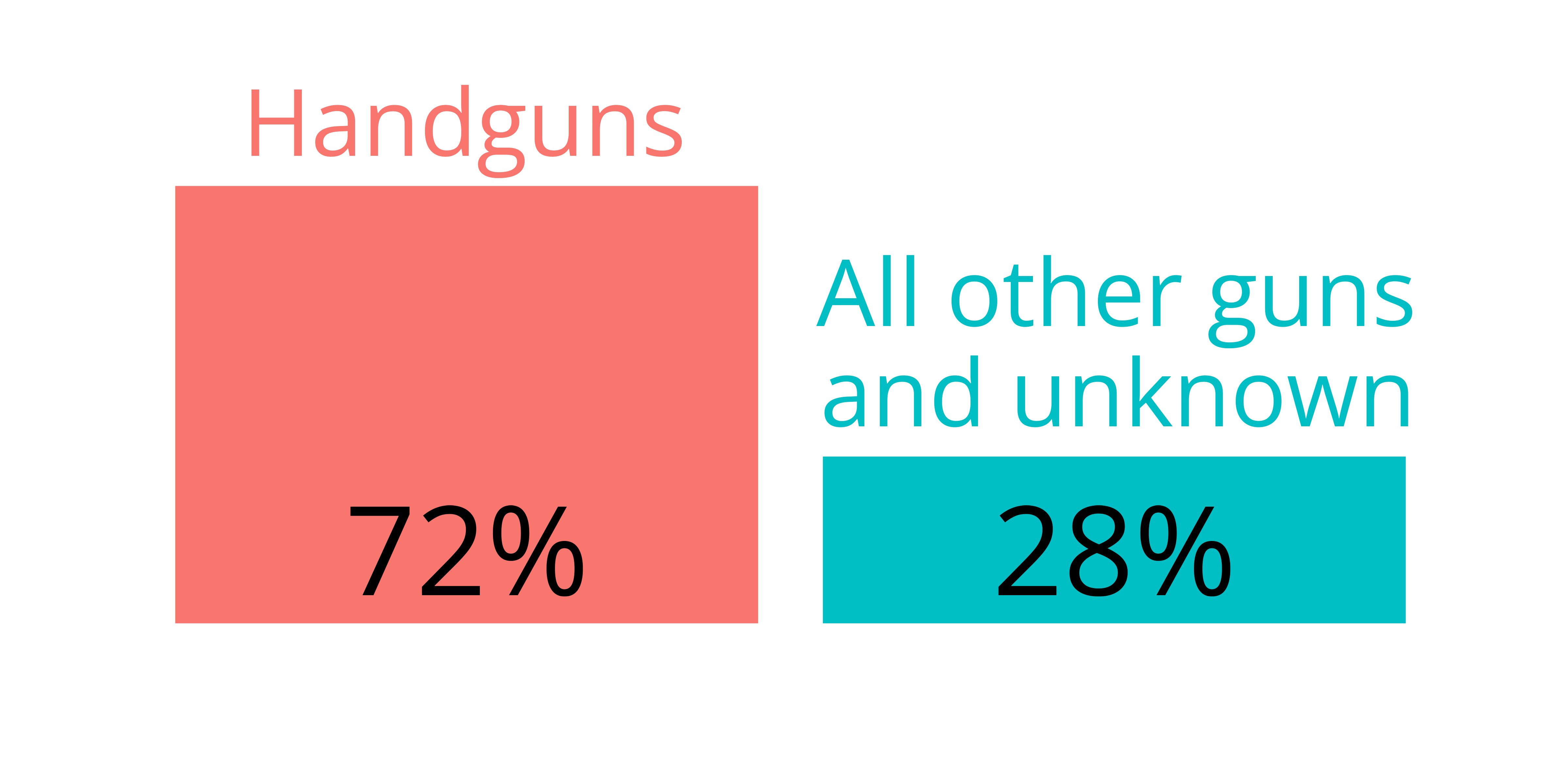
Most handgun violence involves concealed handguns
Handgun violence over the life course
Most concealed handgun research focuses on adolescents
But handgun offending occurs throughout the life course
We know little about gun carrying over the life course
Questions
- When does onset of concealed carry occur?
Is there continuity in carry over the life course?
- Does it differ for legal and illegal carry?
Does exposure to gun violence predict onset of carry?
- Does it differ between adolescence and early adulthood?
- Cohorts born 1981, 1984, 1987, and 1996
- Average ages 25 to 40 in 2021
- Key measures:
- Onset: Age first carried a concealed gun
- Continuity: Carried in past year (wave 5 only)
- Exposure: Age first was shot or saw someone else shot
- Survey and attrition weights
Onset
When does onset of concealed carry occur?
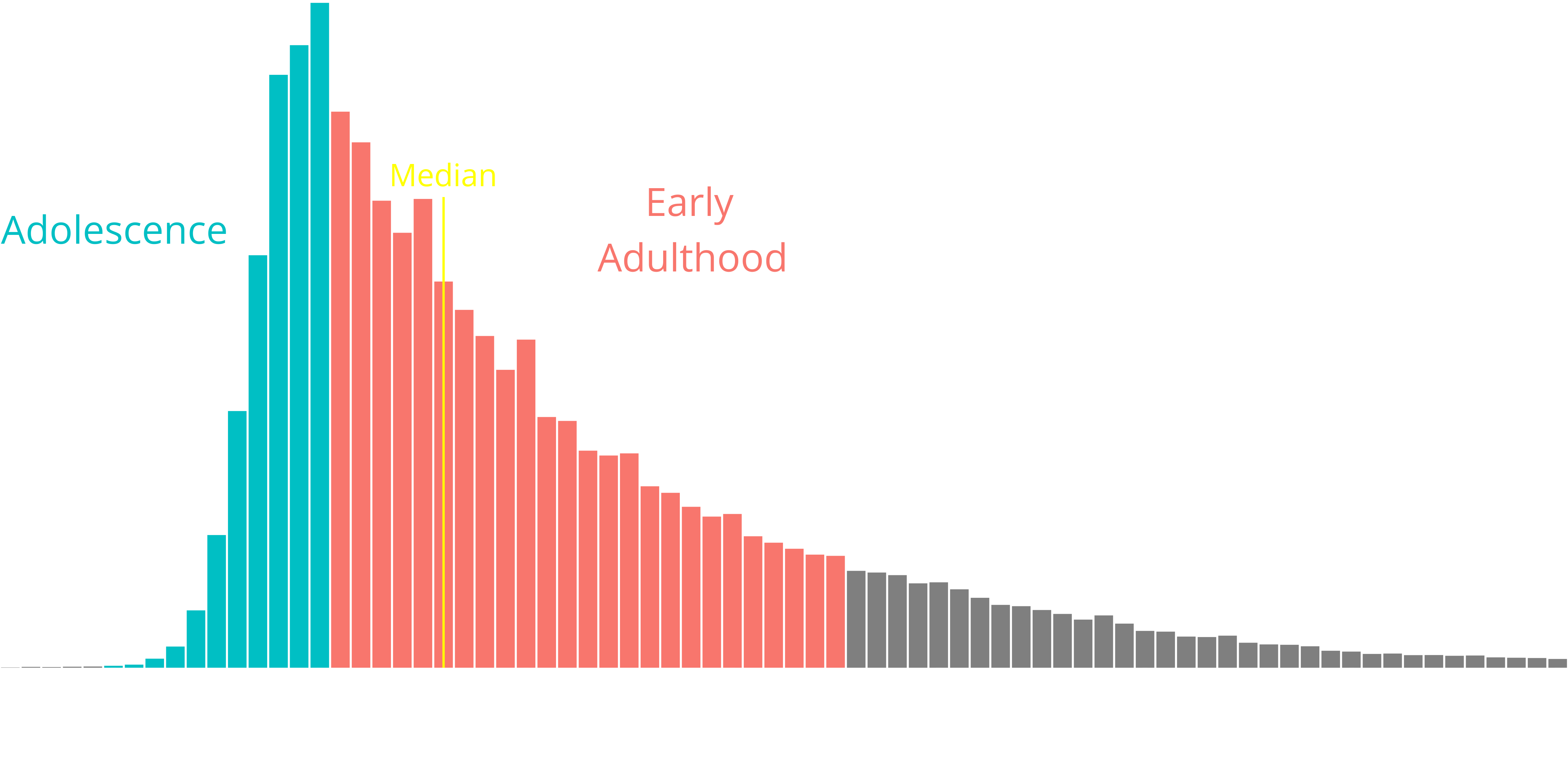
Onset of concealed carry
- Rapid rise in adolescence
- Steady rise throughout early adulthood
Age of first gun use by carry onset
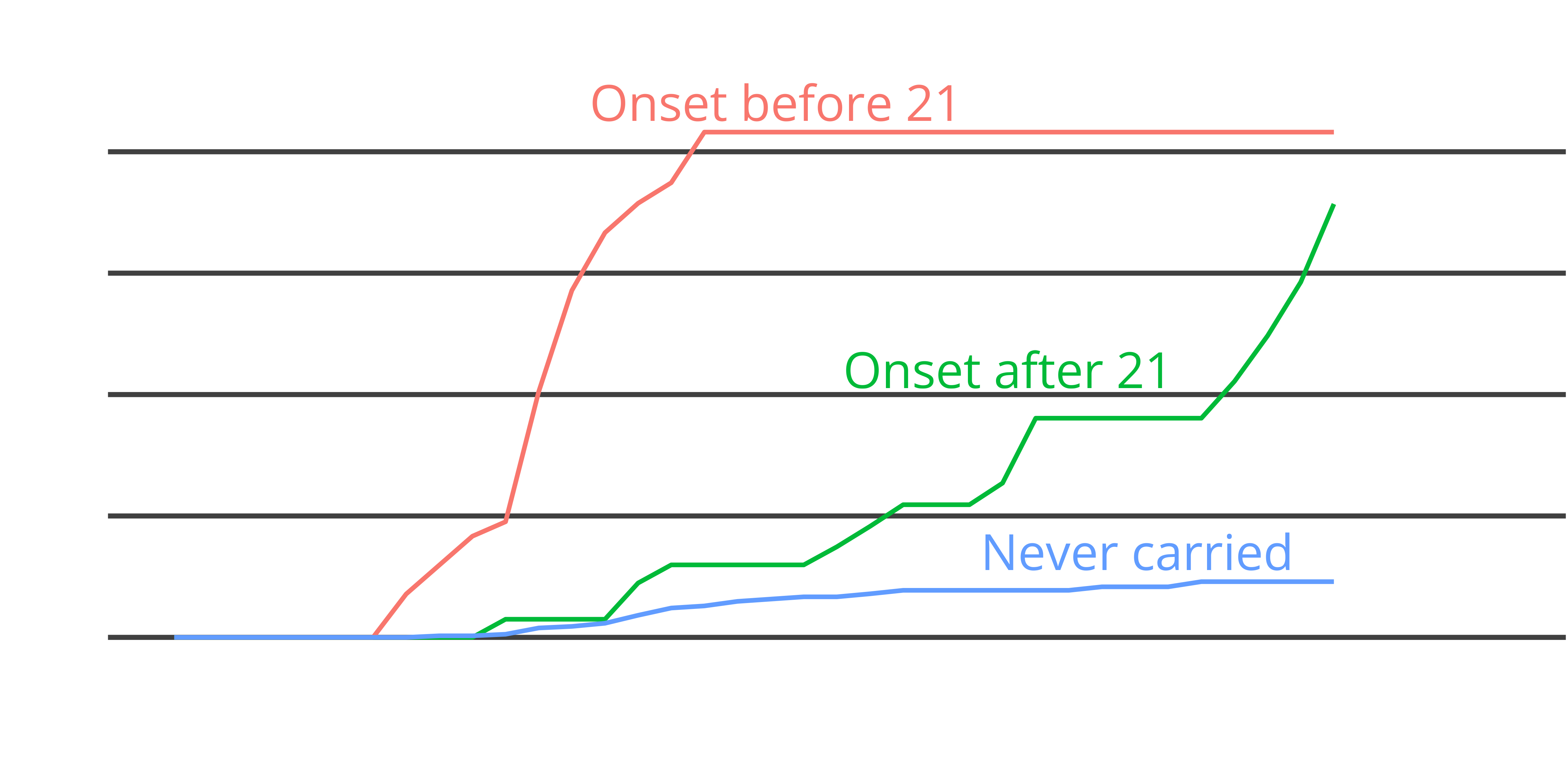
- 42% of young carriers used gun by 21
- Those who didn’t never used a gun later in life
- Lifetime gun use nearly equal by age 40
Continuity
Is there continuity in carry over the life course?
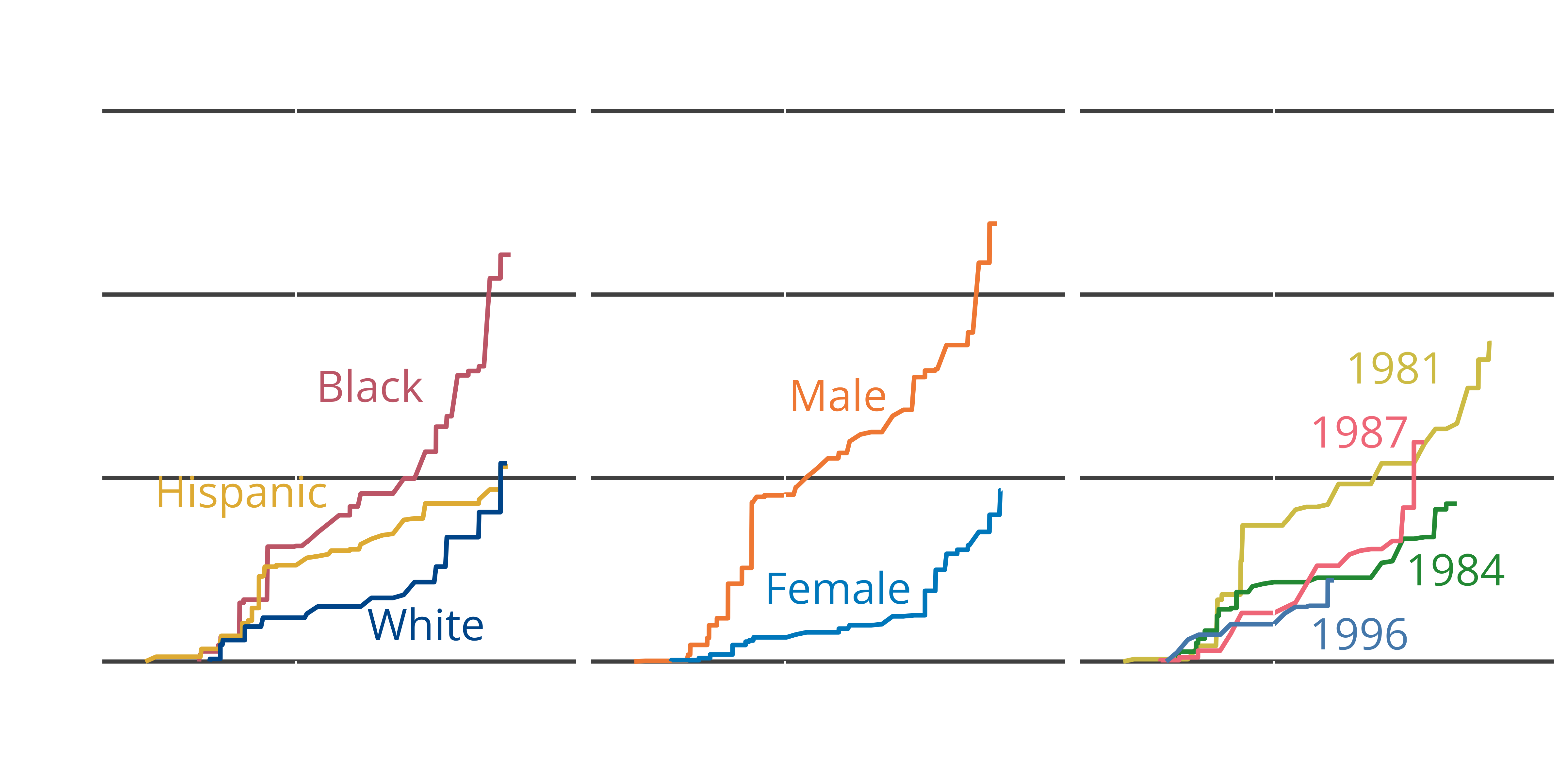
Past-year carry in 2021
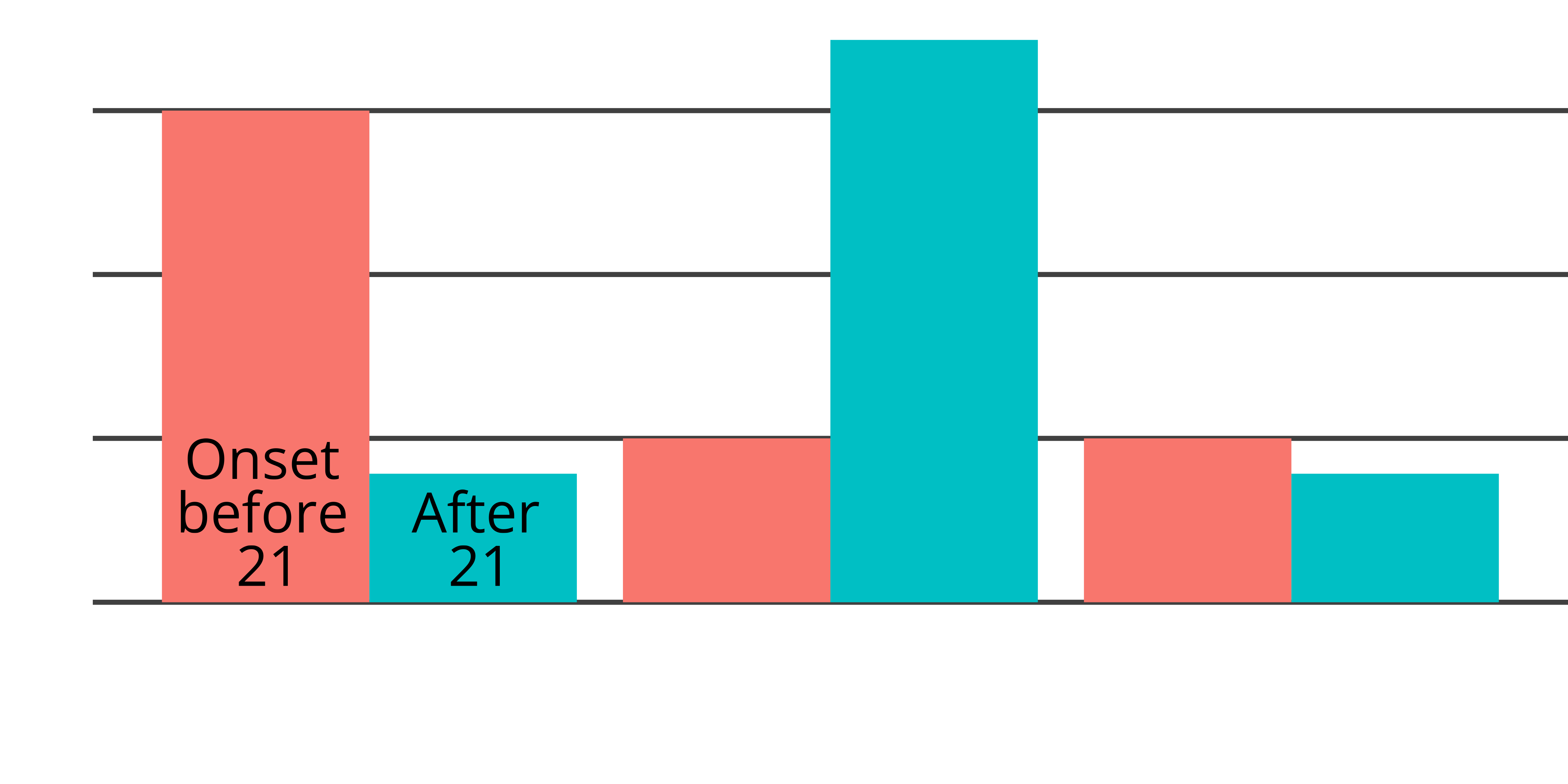
- 60% of young carriers not carrying today
- Young carriers no more likely to carry without permits
Exposure to gun violence
Does exposure to gun violence predict onset of carry?
Exposure to gun violence
Occurs throughout life course but concentrated in adolescence
Implicated as a proximate cause of gun carrying and subsequent use
- Strong evidence for adolescents
- Less evidence for adults
Our counterfactual approach:
- Treatment: Exposure by age \(T_1\)
- Outcome: Carry from age \(T_1\) to age \(T_2\)
- Imputation estimator for censoring

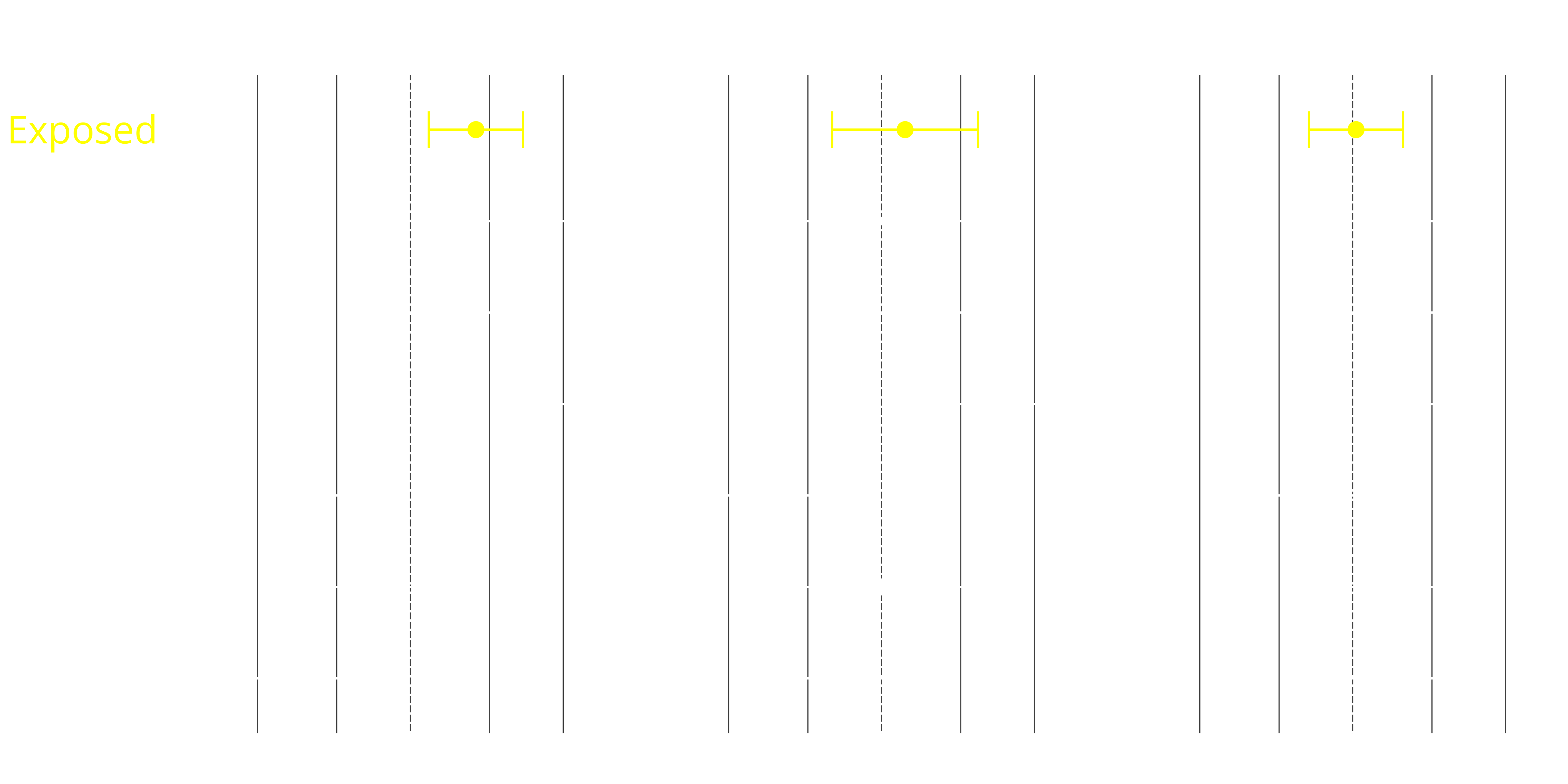
Probability of carry onset by age period
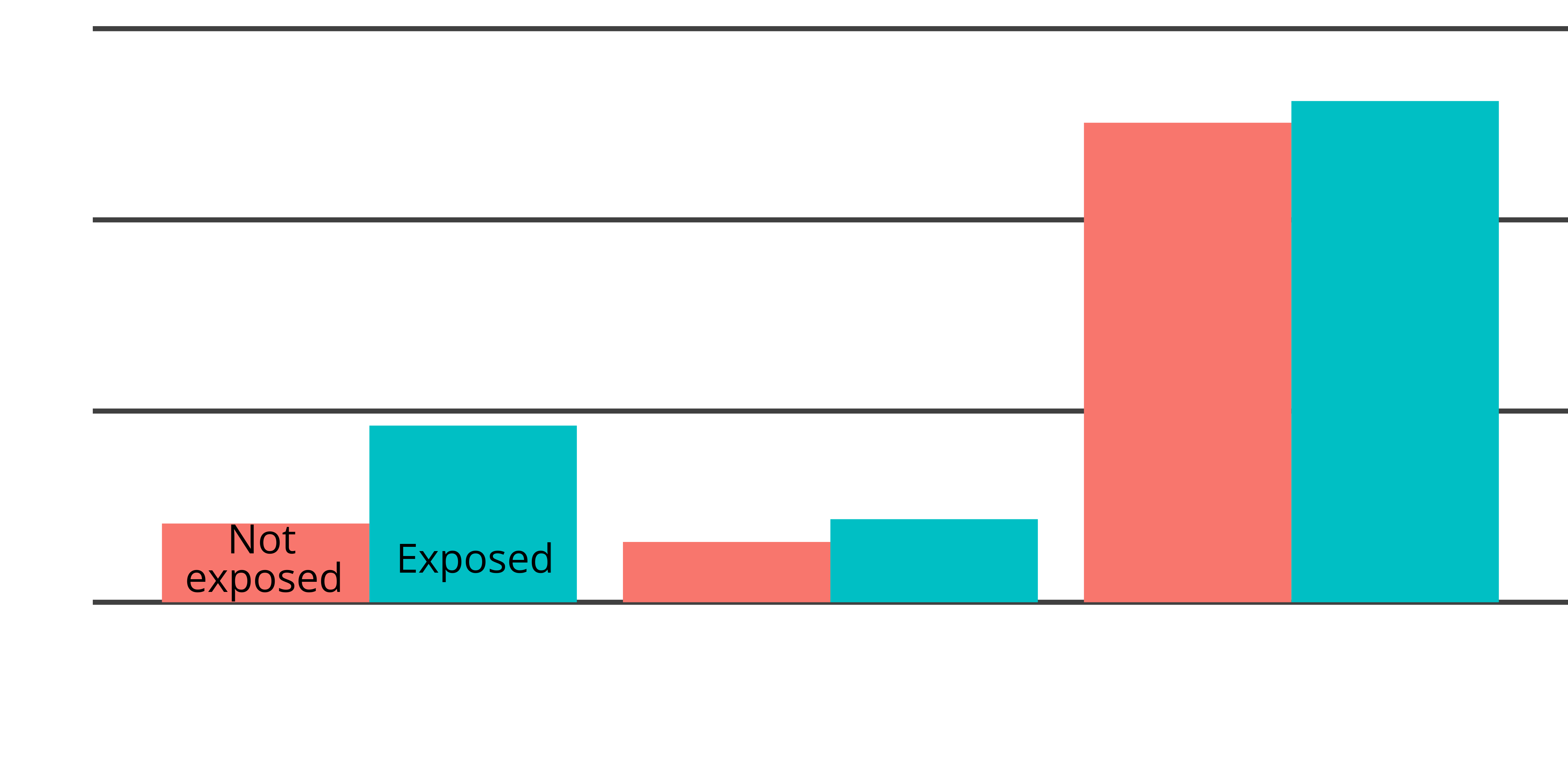
- Carry twice as likely in adolescence among exposed
- No difference in carry in early adulthood
Takeaway: Two Processes
Carry appears to follow two processes:
- Adolescent-onset
- One third of those ever carrying
- Usually age limited
- As is gun use
- Sensitive to exposure
- Adult-onset
- Two thirds of those ever carrying
- Usually persistent
- Gun use accumulates over time
- Insensitive to exposure
New Questions
- What causes selection into each process?
- How does frequency of carry vary within each process?
- How does macro-context impact carrying across life course?
- How does life-course variation in carrying impact rates of violence?
Feedback and Questions
Contact:
Charles C. Lanfear
Institute of Criminology
University of Cambridge
cl948@cam.ac.uk
For more about the PHDCN+:
PHDCN@fas.harvard.edu
https://sites.harvard.edu/phdcn/
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40865-022-00203-0
Appendix
Continuity visualized
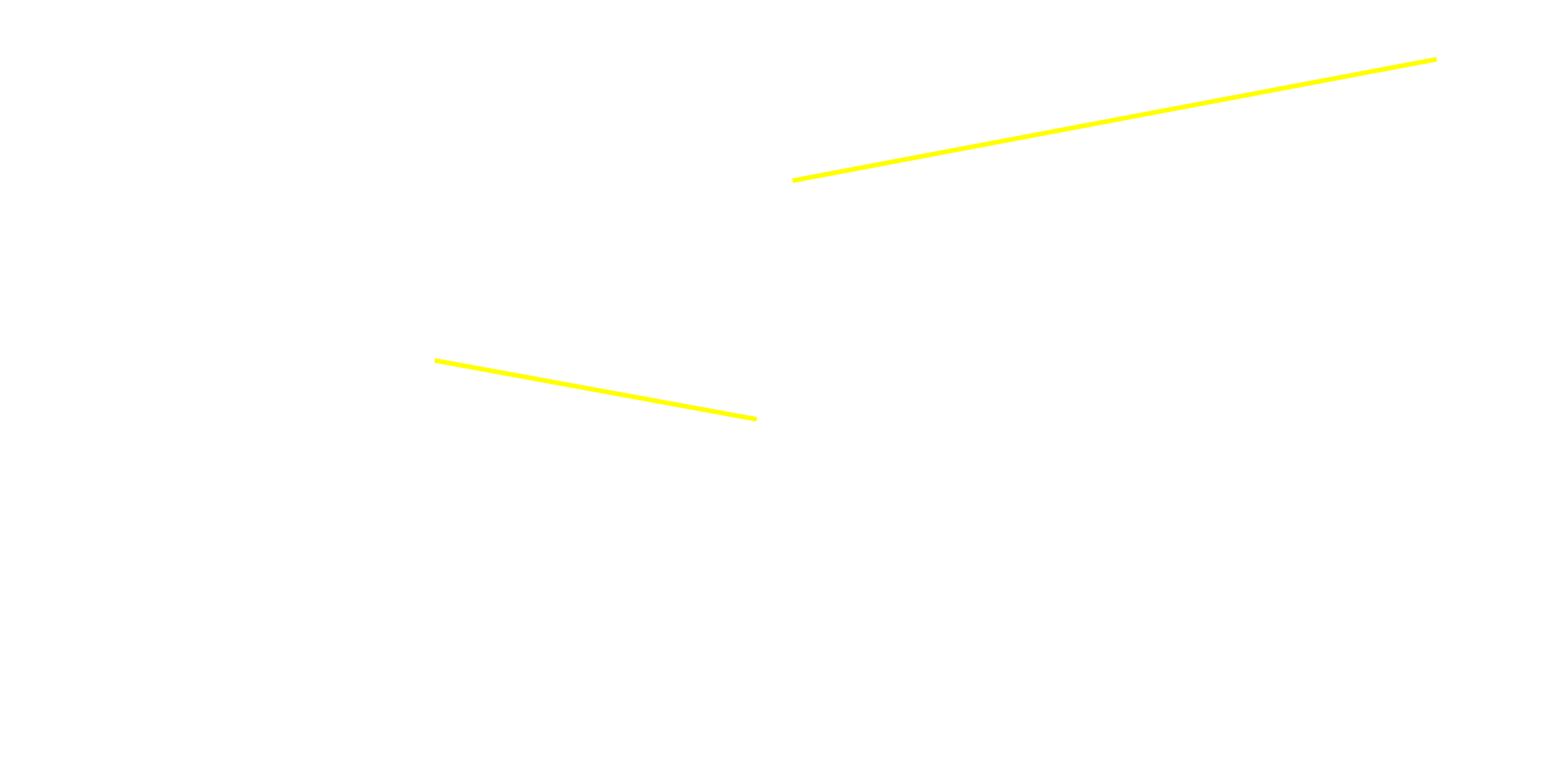
Carry by legality of onset
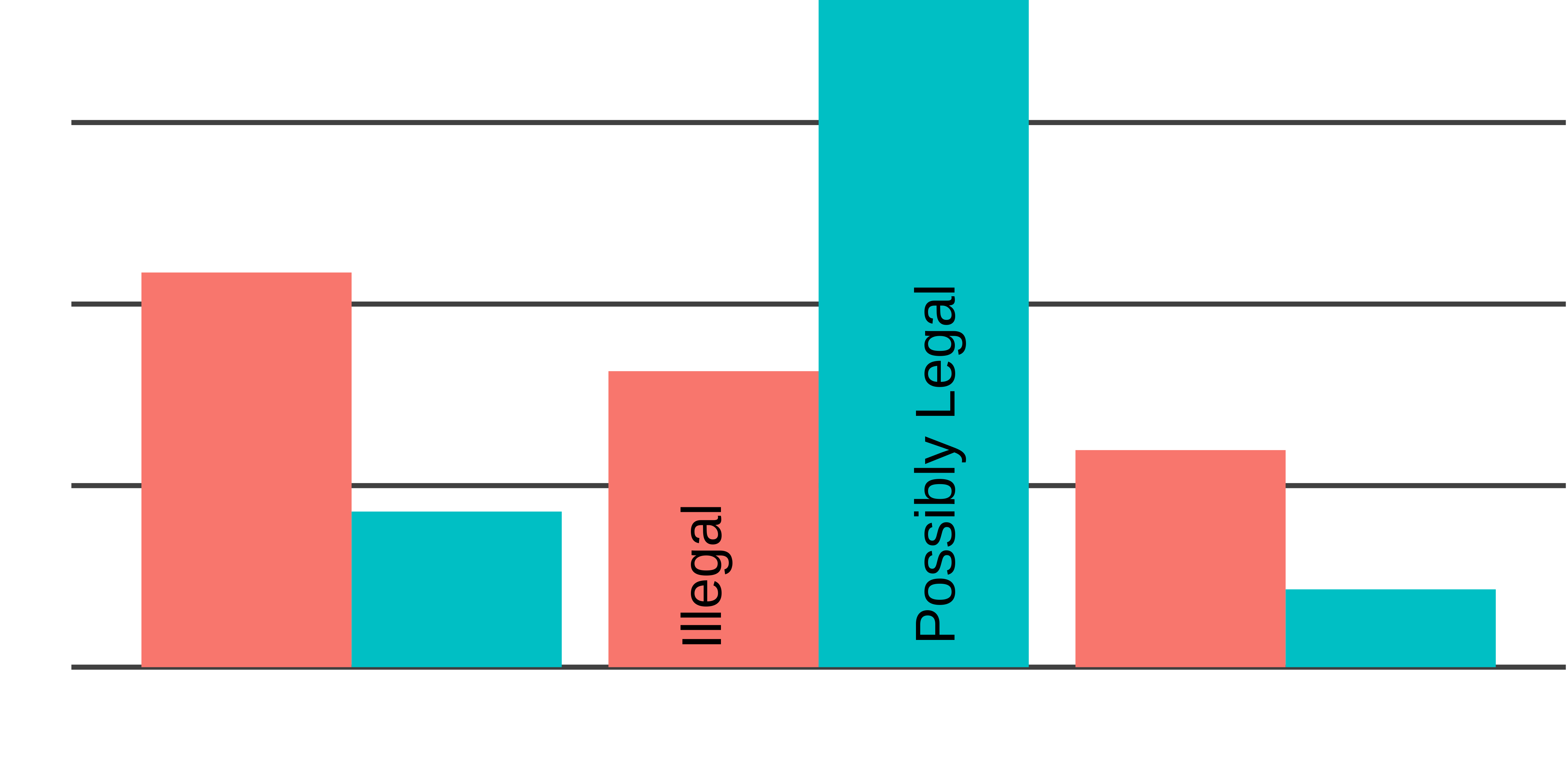
Legality of onset is not clearly identified
Full exposure models